Introduction
Since prehistoric times, it is known to ferment sugary and
other materials to alcohols, extract harmful compounds from the
fermented product and preserve useful ones. However, even in the
industrial manufacture of noble beverages (cognac, brandy) by
distillation, neutralization, purification and other methods, harmful
substances are not completely removed.
During the primary distillation of fermented products, along
with alcohol, a mass of harmful substances, including poisons:
methanol, fuel oils, and other untreated compounds, is also
distilled. The boiling point of alcohol is 78.4 °C, and in fermented
products there are liquids that boil at lower (methanol, acetone,
acetaldehyde, etc.) and at higher temperatures (amyl, propyl,
isoamyl and other alcohols, furfural, acetyl). Many of them
are poisonous and dangerous to humans. However, during the
processing of fermented products with the separation of fractions,
with the removal of the most toxic impurities in the final product,
there are still quite a lot of harmful components called fuel oils. In
a high-quality alcoholic liquid should contain as little fuel oils but
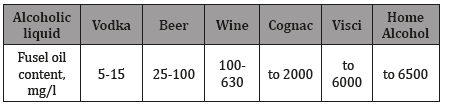
should be kept harmless substances. The approximate content of
fuel oils in some products (Table 1).
Table 1: Approximate content of fuel oils in alcoholic liquids.
Fuel oils contain high-molecular alcohols, which are difficult to
break down due to the complex composition of the human body.
Therefore, the work human liver is complicated, the decontamination
of toxins is slowed down, as from the management of the extended.
To break down substances, they must be oxidized by blood oxygen.
But the longer their molecules are, the more oxygen they need.
When using large doses of alcohol blood supply is difficult, oxygen
is not enough, so the toxins are not completely oxidized. In this
case, things are formed more poisonous than methyl alcohol. With
a large content of acetaldehyde, the possibilities of the liver to
neutralize ethanol are sharply reduced, its proces-sing is delayed, and
the concentration of acetaldehyde increases several times due
to its further formed during the decay of ethanol.
In General, the product obtained after distillation of the initial
fermented and fermenting substances contains impurities divided
into groups:
1. Hats with a boiling point of 78.4 °C below: acetic-butyric
ether, acetaldehyde, acetone.
2. Intermediate, as main components.
3. Tail (fuel oil) with a higher boiling point and lower
volatility than ethyl alcohol: monoatomic alcohols: propyl,
isopropropyl alcohol and its isomer, propanol-1, amyl, isoamyl,
isobutyl and methyl alcohols, furfural, acetyl, ethyl acetate,
ethyl butyrate and other toxic compounds; the most dangerous
of them isoamyl alcohol (isoamyl alcohol C5H4OH), giving up to
60% of the volume of fuel oils.
In fuel oil are also found: n-propyl, n-butyl, hexyl alcohols,
diethyl ether, methyl acetate, methylpropionate, diacetyl, as well as
acids: acetic, propionic, isobutyric, n-oil, isovalerian, n-valerian and
more than 40 substances. And Isabella grapes during fermen-tation
also produces hydrocyanic acid.
The largest amount of fuel oils produced from grain raw
materials, when the alcohol raw them of 0.2-0.4%. The content
of fuel oils in vodka is limited by standards: for vodka «special
purification»-no more than 15.0mg/l, for vodka «extra» up to
10.0mg/l, for vodka «Lux»- 5.0mg/l. In 0.5 liters of «normal» vodka
on average contains 4ml of fuel oil. Especially dangerous isopropyl
alcohol, which as its «cuts» a person, turns off consciousness, and
possible death. For the average person, 1.5 liters of ordinary vodka
is enough to get a lethal (13-15ml) dose of fuel oil.
Methods of cleaning from fuel oils: It is mainly used
rectification of liquids, i.e. their separation into components
(fractions) substances with a close boiling point. To do this, the
liquid is heated to the boiling point and evaporation of the first
fraction, it is kept heated and the first fraction is extracted by vapor
condensation. Further, the temperature for evaporation of the
second fraction is increased and it is similarly extracted as a useful
raw material. After that, the distillation can be stopped.
The industrial method of cleaning from fuel oils is carried out
in distillation columns in vertical cylindrical vessels of constant or
variable cross section, equipped with heat and mass transfer devices
and auxiliary units for the separation of liquids into fractions. The
heated liquid is fed into the column from below, the light fractions
are concentrated in the upper part of the column, and the heavy
ones with a higher condensation temperature are concentrated in
the lower part. Lack of rectification is the duration, complex, very
сu-mbersome installation, high costs of thermal energy.
In private, alcohol purification is used by entering 3-5g/l of
potassium permanganate (KMnO4) into them, settling for up to
10 days, precipitating a dark precipitate and draining the liquid
without sediment. Enter also on 50g/l of wood activated carbon of
industrial brands, defend liquid of 20-30 days, filter through paper
or cotton filters with the activated carbon. Apply and freezing
harmful substances, their deposition and draining the liquid
without impurities. These long-term processes require freezers
and other devices, special substances.
Innovation in alcohol purification:Tambov state technical
University to clean alcohol from fuel oils tested combined static
mixer-activator according to Russian patent No. 2411074 [1]. The
peculiarity of the activator is that: it carries out mechano-chemical
dispersion of long-chain organic liquids, passed through it [2,3].
The use of the activator simplifies the process, reduces the content
of sea-wool oils by at least 10-13%, some toxic substances in simple
waters up to 3 times, esters by at least 8 times (Figure 1).
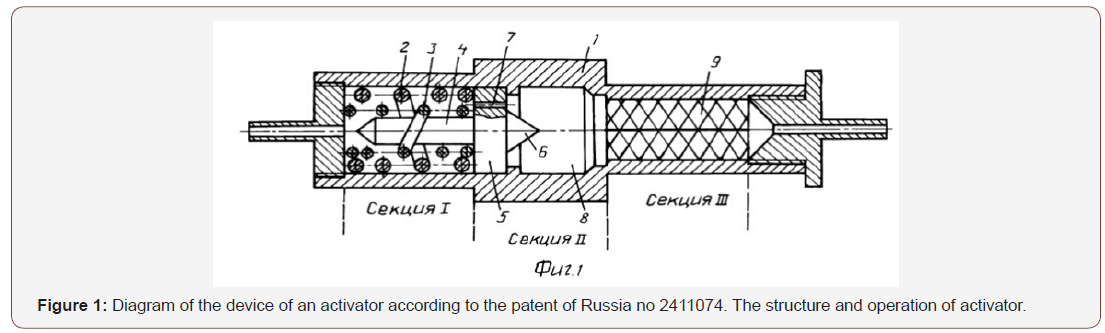
In the cylindrical housing 1 of the activator there are sections
chambers I, II, III. In the section of the chamber I mounted the screws
2 and 3. The screw 2 is adjacent to the inner surface of the housing
1 and has a right side or left side winding. Inside the screw 2 with
a small gap mounted screw 3 with the opposite winding. Inside the
screw 3, also with a small gap, a rod 4 is mounted, combined with a
disk 5 having a cone 6 on the reverse side.
In disk 5 microchannels 7 are made, the centers of which are
located in the gap bet-ween the screws 2 and 3. For a disk 5 is
mounted the second (II) cavitation section 8, followed by section-
III camera, which features a lattice design 9 with a narrow slit
width of 0.1-0.5μm, At the beginning, the liquid is controlled on a
chromatograph for the initial content of harmful substances, then
heated to 25-28 °C. Setting the flow rate of the 10cm/s, pump it through
the activator. In it, in the first chamber, clusters of fuel oils
are rubbed with vortex counter flows between the external and
internal screws. Then the liquid is injected through microchannels
into the second vacuum chamber rarefaction, where the molecules
of the oils are dispersed cavitation. Finally, the liquid is pumped
through the broken slots of the structure 9 of the third chamber,
which finally disperse and activate the molecules of fuel oils and
provide further activation of alcohol for a long period.
Therefore, liquids are kept for up to 30 days, the third time
they control the content of fuel oils and when they are reduced by
at least 10%, they are given a liquid for processing or a finished
product. Activation of alcoholic liquids not only reduces the content
of fuel oils, but also increases the content of useful components in
them.
Examples of testing method: 21.02.2018 «Cognac» checked
on the content of organic components on the gas chromatograph
«Cristallux-4000M» (with column HP-FFAP 50 mx0/32x50um
and detector PID-1) in Tambov certified laboratory of forensic
and medical examination. Then the drink was pumped through
the activator and similarly checked the content of the components
(Tables 2,3).
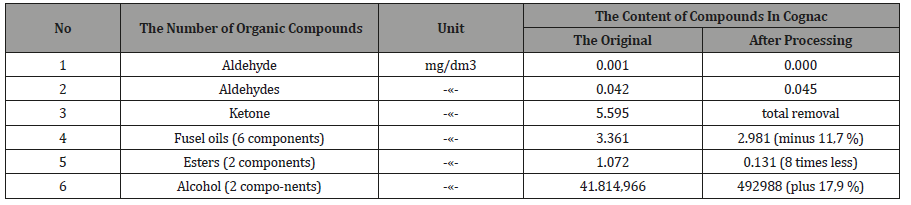
Table 2: Complete results of the control components in cognac.
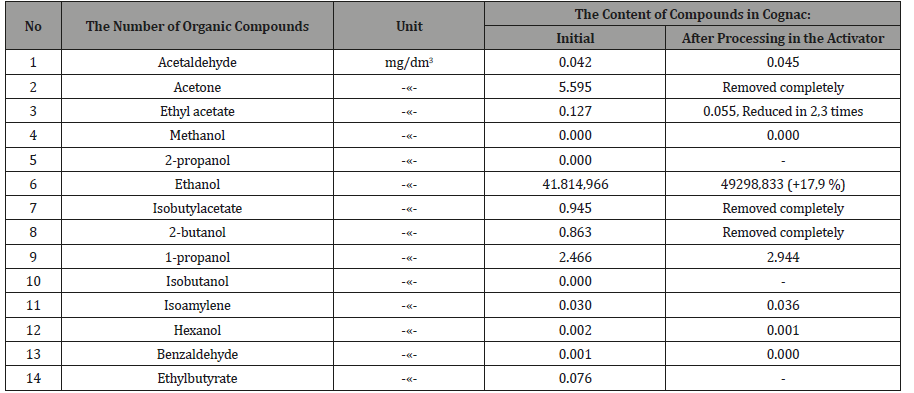 Table 3:
Table 3: Summary results of control of components in cognac, The summarized results of the control components in brandy.
18.04.2018 vodka production was similarly tested on the
content of toxic components, after which it was pumped through
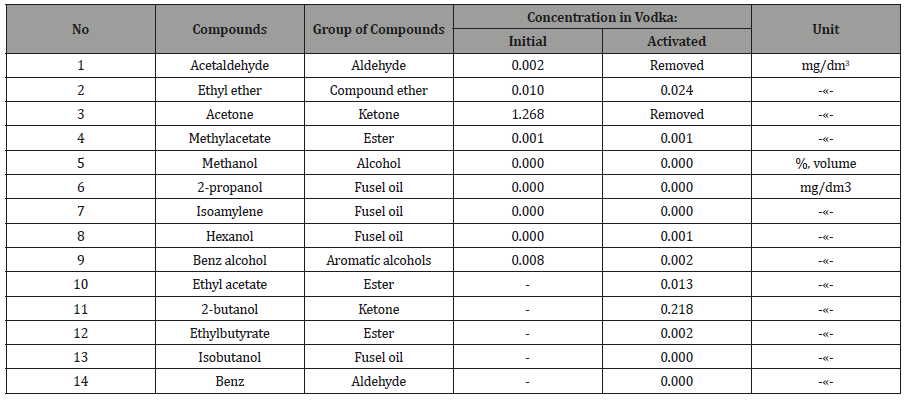
the actuator and checked again (Table 4, 5). From Tables 2-5 it
follows, that activated the «Cognac» acetone, ketone, the isobutyl
acetate and 2-butanol is completely removed, ethyl acetate is
reduced in 2,3 times, the six components of oil decreased by 11.7%,
the two components of esters 8 times, and the two components of
the alcohols increased by 17.9%. Similarly, in vodka acetaldehyde
and acetone are removed, aromatic alcohols were less than 4 times
that of the ketone at 5,9 times.
Table 4: Approximate content of fuel oils in alcoholic liquids.
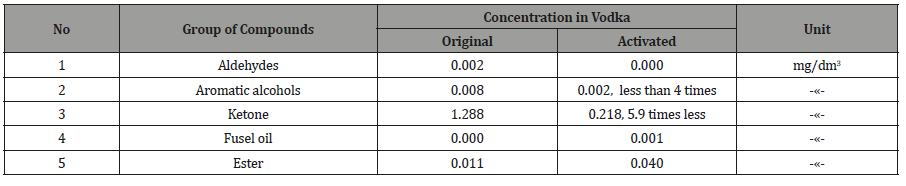 Table 5:
Table 5: Changes in vodka content of organic compounds.
Other testing results
1. In the wine «Cabernet» after activation the content of
fuel oils decreased from 2,3mg/dm3 to 0,971mg/dm3, i.e. 2,37
times.
2. In white dry wine-3 times.
3. And in sweet fortified wine-100 times.
Acknowledgment
None.
Conflict of Interest
No conflict of interest.